Participe au Veggie Challenge !
Lisez les dernières nouvelles ici, ou parcourez les pages suivantes pour découvrir toutes nos initiatives en Belgique.
Notre raison d’être
ProVeg est la première organisation internationale spécifiquement dédiée à l’alimentation végétale. Notre ambition : diviser par deux la consommation mondiale de produits animaux d’ici 2040. Parce que c’est essentiel pour notre planète, notre santé, les animaux et l’humanité en général.
Pour parvenir à cet objectif, nous inspirons les citoyens, formons et conseillons les professionnels, les guidant vers une transformation durable. Nous sommes des catalyseurs de l’innovation et nous soutenons la recherche et la créativité pour porter de nouvelles façons de penser et de consommer. De plus, nous sommes impliqués dans la détermination des politiques publiques afin de soutenir un changement structurel vers une plus alimentation végétale. Au cœur de notre démarche se trouve la construction d’une communauté unie, partageant une passion pour un avenir meilleur.
Notre impact
Campagnes réussies
Plus de 10 % des Belges ainsi que de nombreuses écoles, entreprises et villes participent à notre campagne la plus célèbre, le Jeudi Veggie. Grâce au VeggieChallenge qui a lieu chaque année au mois de mars, un Belge sur huit mange davantage veggie ou végane.

ProVeg inspire le grand public
Nous facilitons le choix de produits d’origine végétale pour les consommateurs en les aidant à faire leurs premiers pas via nos campagnes, nos événements, nos recettes, des conseils nutritionnels, des astuces culinaires et de l’inspiration. Nous mettons à disposition la plus grande base de données gratuite de recettes végétales en Belgique et nos campagnes comme le Veggie Challenge ou le Jeudi Veggie permettent à des dizaines de milliers de Belges de manger davantage végétal.
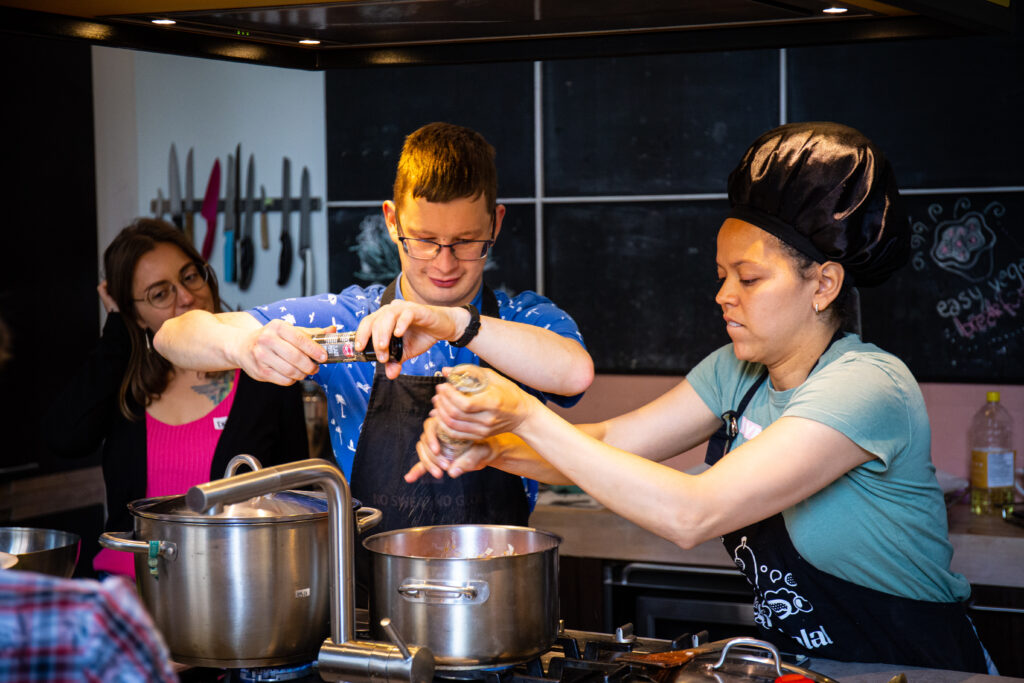


Veggie Challenge
Mars, c’est le mois du Veggie Challenge ! Rejoignez-nous ainsi que des milliers d’autres Belges et relevez le défi d’une alimentation plus végétale.

Jeudi Veggie
Explorez de délicieuses recettes, faites le plein de trucs et astuces, et découvrez les nombreux bienfaits d’une assiette végétale, un jour par semaine. Plus de 10 % des Belges ont déjà participé !
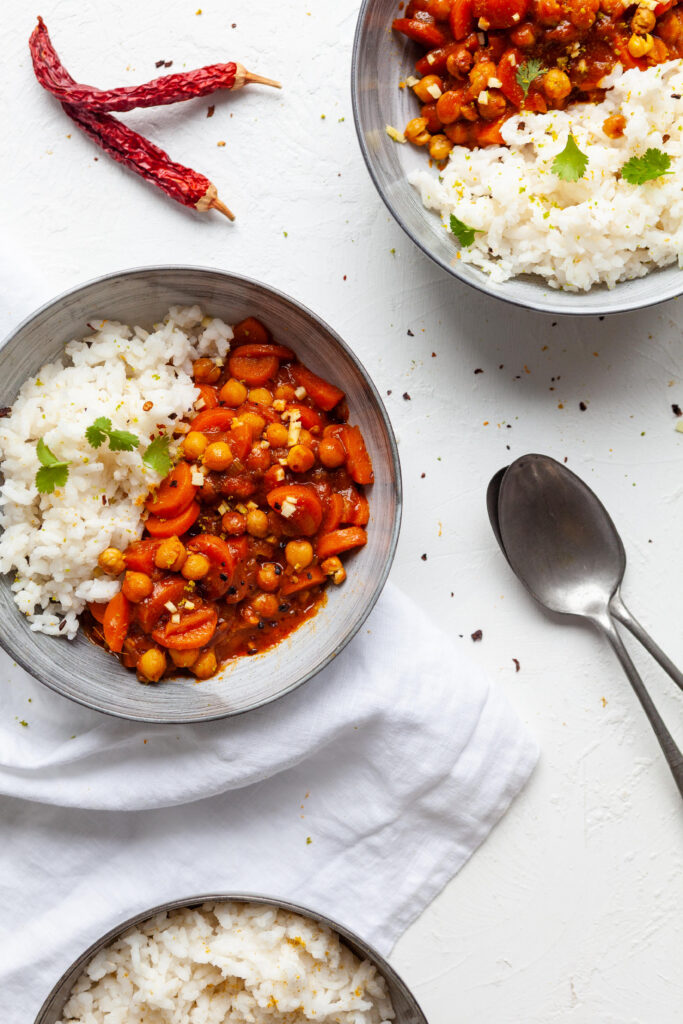

Base de données de recettes
Découvrez des centaines de recettes végétales gratuites pour chaque moment de la journée ! Filtrez par niveau de difficulté, recherchez par ingrédient spécifique ou trouvez l’inspiration dans nos publications et collections.
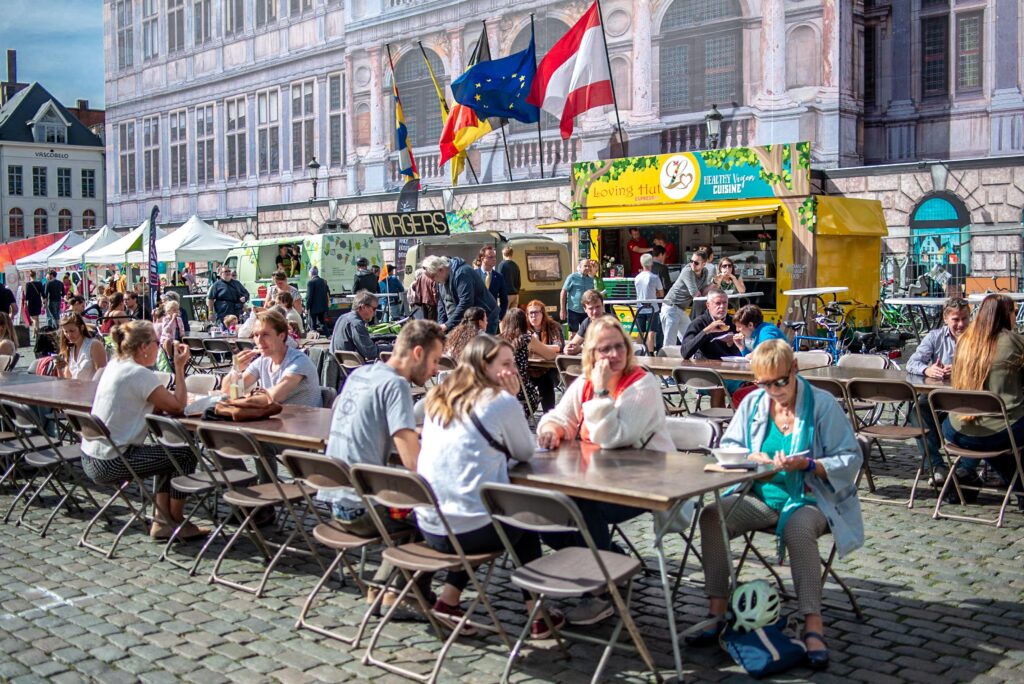

Événements
En collaboration avec nos groupes locaux, nous organisons des événements autour du végétal près de chez vous et ailleurs. Consultez le calendrier ci-dessous.
N’hésitez paz à consulter notre agenda d’activités Jeudi Veggie à Bruxelles.
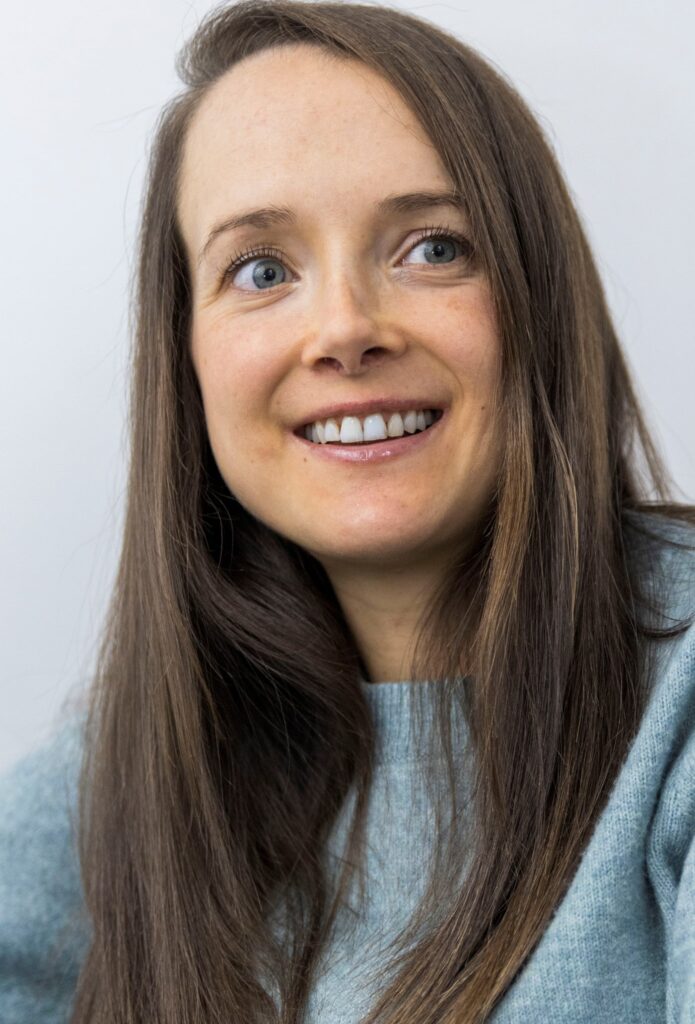

Conseils nutritionnels
Rencontrez notre diététicienne
Notre diététicienne répond à toutes vos questions relatives à la santé.

Trucs, astuces & FAQ
Toutes les réponses à vos questions
Où puis-je trouver des produits végétaliens abordables ? Que dois-je absolument avoir dans mes placards ? Comment manger végétalien en voyage ? Obtenez toutes les réponses à vos questions, découvrez des trucs et astuces et téléchargez nos publications gratuites.

Nos publications
Découvrez nos e-books et posters gratuits
Téléchargez nos livres de recettes, nos posters nutritionnels et nos infographies avec tout ce que vous devez savoir sur l’alimentation veggie.
ProVeg innove
ProVeg International soutient les start-ups végétales du monde entier. Grâce au ProVeg Incubator, nous organisons chaque année plusieurs programmes de développement dans le cadre desquels nous fournissons aux jeunes entreprises la formation, les compétences et les contacts dont elles ont besoin pour assurer le succès de leur entreprise ou de leur produit. Pour en savoir plus sur la manière dont vous pouvez participer en tant que start-up, mentor ou investisseur, lisez-en plus ici.

ProVeg œuvre pour plus de végétal

ProVeg collabore avec les décideurs politiques, les gouvernements, les institutions publiques, l’industrie alimentaire, le secteur médical et scientifique et les médias pour faciliter le choix d’une alimentation végétale.
Avec le réseau Next Food Chain, ProVeg et ses partenaires font pression contre les directives qui tendent à limiter l’utilisation des termes relatifs à la viande pour les substituts végétaux en Belgique. Avec nos collègues de ProVeg International, nous avons également l’opportunité de faire du lobby concernant la politique climatique et alimentaire européenne.
Ensemble pour un futur basé sur les plantes
ProVeg crée des communautés

Les bénévoles ProVeg
Grâce à notre vaste réseau de plus de 400 bénévoles et nos groupes de bénévoles locaux, vous trouverez toujours des activités intéressantes dans votre région. Envie de devenir bénévole? Contactez [email protected]
Les supporters ProVeg
Bienvenue dans notre club de Supporters ProVeg ! Grâce à votre soutien, nous construisons un monde dans lequel chacun peut choisir une alimentation saine et savoureuse, qui soit aussi bonne pour les animaux, la planète et chacun d’entre nous.
ProVeg accompagne les entreprises & le secteur de la restauration
ProVeg rassemble tous les acteurs qui influencent les choix alimentaires que nous faisons. Nous collaborons avec des entreprises, producteurs, distributeurs, innovateurs, chefs … en construisant un réseau pour la transition alimentaire. Nous réalisons des études de marché sur les habitudes alimentaires des Belges, nous accompagnons les producteurs dans le développement et la promotion de produits végétaux et nous formons des chefs et cuisiniers professionnels pour améliorer le développement et la commercialisation de repas végétaux.

Études de marché
ProVeg publie régulièrement des études de marché, des analyses de tendances et des rapports d’expertise. Consultez toutes nos publications au niveau belge et international.
Belgique
- L’écart de prix se réduit entre les produits végétaux et leurs équivalents d’origine animale — Enquête réalisée par Questionmark auprès de 5 enseignes de supermarchés en Belgique (2023)
- « Le nombre de végétariens et végétaliens continue d’augmenter. »
– Statistiques (2022) sur les habitudes alimentaires en Belgique, enquête bisannuelle en collaboration avec iVOX - « Albert Heijn est le supermarché le plus vegan friendly de Flandre et Bruxelles »
– Classement des supermarchés, étude semestrielle réalisée par EVA/ProVeg, BE Vegan & Bite Back (2022)
International
- La moitié des Européens réduisent leur consommation de viande

Services aux entreprises
Accompagnement sur mesure
Nous travaillons avec les fabricants et distributeurs pour identifier leurs besoins et opportunités, leur fournir des recommandations stratégiques personnalisées et un soutien dans leurs objectifs commerciaux.
Intéressé ? Contactez-nous à l’adresse [email protected].
Partenariats commerciaux
ProVeg Belgium touche un large public de flexitariens, végétariens et végétaliens. Élargissez votre groupe cible pour vos produits végétaux grâce à une collaboration commerciale. Diffusez vos publicités dans nos médias, devenez partenaires de l’une de nos campagnes ou faites la promotion de vos produits via nos réseaux sociaux.
Pour connaître toutes nos solutions de partenariat, prenez contact avec Annemarie à l’adresse [email protected].
Certification V-Label
En tant que gestionnaire et organe de contrôle du V-Label en Belgique, nous guidons les consommateurs dans le choix du végétal. Grâce à notre expertise et notre savoir-faire, nous apportons confiance, transparence et clarté aux consommateurs. En tant que producteur, le V-Label vous permet d’accéder à de nouveaux marchés, d’instaurer la confiance auprès de votre public cible et de booster la visibilité de vos produits.
Vous souhaitez bénéficier du V-Label sur vos produits ? Découvrez toutes les infos ici ou contactez-nous à l’adresse [email protected].
Réseau d’affaires Next Food Chain
Grâce au premier réseau d’entreprises actives dans l’alimentation végétale en Flandre, nous œuvrons pour que le choix de l’alimentation végétale devienne une évidence. Nous rassemblons les acteurs de l’ensemble de la chaîne alimentaire et initions une nouvelle dynamique du champ à l‘assiette. Il peut s’agir d’acteurs issus de toutes les étapes de la chaîne : des producteurs et transformateurs de légumes aux producteurs de substituts végétaux à la viande ou aux produits laitiers, en passant par les distributeurs et les traiteurs.
Vous souhaitez devenir membre ? Contactez-nous à l’adresse [email protected].

Services pour la restauration
Ateliers végétaux sur mesure
Nos chefs professionnels sont là pour organiser des ateliers ou prodiguer des conseils adaptés au sein de votre école hôtelière.
Vous souhaitez former votre équipe de chefs ou les professeurs de votre école hôtelière à la cuisine végétale ? Envoyez un e-mail à [email protected].
Découvrez ici ce que nous pouvons faire pour vous.
Outils gratuits pour les professionnels de l’alimentation
Découvrez plus d’une centaine de recettes, téléchargez notre guide plein de conseils culinaires et d’informations sur les produits ou faites le plein d’inspiration sur notre blog… tout pour écrire la future success-story végétale pour votre cuisine.
À propos de ProVeg Belgium
Notre organisation
ProVeg Belgium est l’évolution logique de l’association EVA vzw, l’asbl belge qui œuvre depuis 2000 pour un monde davantage tourné vers le végétal. En rejoignant le réseau international ProVeg, nous avons la possibilité d’accroître notre impact, non seulement en Belgique, mais aussi à l’étranger.

Nos partenaires